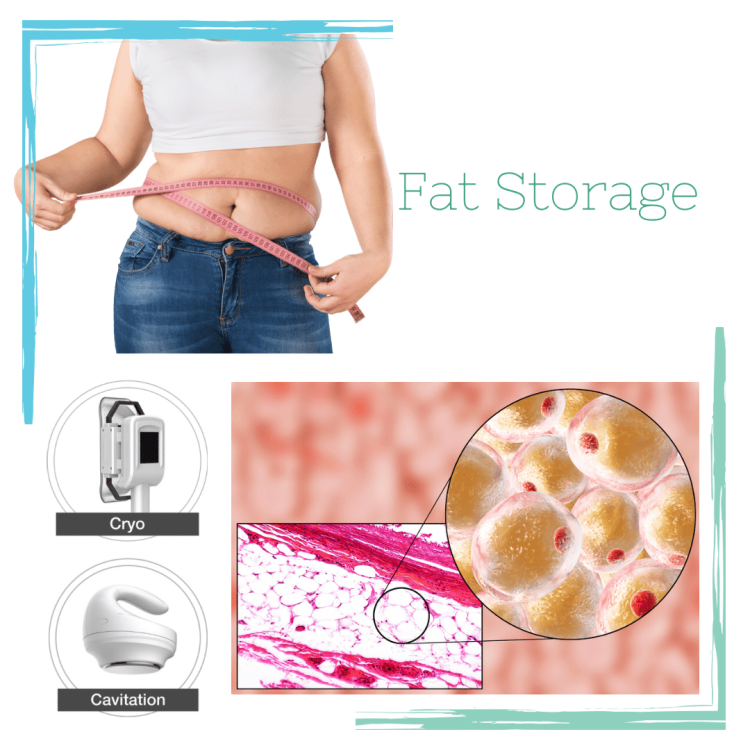
Fat Cells and Fat Storage
Fat Cells and Fat Storage. We all know about fat and have an opinion on it. But do we understand how fat is stored and what it is used for? Here we look at the basics of fat cells.
Fat is essential. It provides energy for our bodies; it provides insulation and protection around our organs and ensures we can digest fat-soluble vitamins.
Fat is stored in fat cells; a typical infant will have around 5 or 6 billion fat cells. A healthy adult will generally have25-30billion. Once an adult becomes classed as overweight, the number can rise to 75million, and an obese person will have 250 million to 300 million.
Inside each fat cell are triglycerides. This is the form that fat is stored in the body. Cells fil with triglycerides as a reserve of energy for the body. If the triglycerides are not depleted, each cell will continue to fill. Once it reaches 4 x its original size, it will multiply by creating a new fat cell. The process will then start again. Create more fat cells to be filled with triglycerides. If the energy consumed by a person is greater than the energy expended, the body will continue to store it in its fat cells. Thus, a person will gain weight.
Fat Cells and Fat Storage: Factors That Infulence Fat Cells
Several factors influence fat cells and their function within the body:
- Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in determining an individual’s predisposition to storing fat. Genetic variations can impact factors such as metabolism, hormone regulation, and fat distribution, influencing how easily fat cells accumulate and store lipid molecules.
- Dietary Habits: The types of foods consumed and overall dietary habits can profoundly affect fat cell function. Diets high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and unhealthy fats can promote fat accumulation and contribute to the expansion of fat cells. Conversely, diets rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats may support better fat metabolism and storage regulation.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity and exercise play a crucial role in regulating fat cell function. Exercise helps increase energy expenditure, promoting the breakdown of stored fat for fuel and reducing the size of fat cells. Additionally, resistance training can help build lean muscle mass, which can increase metabolic rate and support fat loss over time.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormones such as insulin, cortisol, leptin, and adiponectin play key roles in regulating fat cell metabolism and storage. Imbalances in hormone levels, often influenced by factors like stress, sleep deprivation, and certain medical conditions, can disrupt fat cell function and contribute to weight gain and obesity.
- Stress Levels: Chronic stress can impact fat cell function and metabolism through its effects on hormone levels, particularly cortisol. Elevated cortisol levels can promote fat storage, especially in the abdominal region, and may contribute to visceral fat accumulation over time.
- Sleep Patterns: Inadequate sleep or poor sleep quality can disrupt hormone regulation, including hormones involved in appetite control and fat metabolism. Sleep deprivation may lead to increased hunger and cravings for high-calorie foods, as well as impaired insulin sensitivity, which can contribute to weight gain and fat storage.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) found in certain plastics, pesticides, and pollutants may influence fat cell function and contribute to obesity. These chemicals can disrupt hormone signaling pathways involved in fat metabolism and storage.
- Medications: Some medications, such as certain antidepressants, antipsychotics, corticosteroids, and antidiabetic drugs, may affect fat cell metabolism and contribute to weight gain or changes in fat distribution as a side effect.
Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices to support healthy fat cell function and promote overall well-being. By adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, prioritizing quality sleep, and minimizing exposure to environmental toxins, individuals can optimize fat cell metabolism and support their weight management goals.
Fat Cells and Fat Storage: Distribution of fat
Fat distribution in the body refers to the pattern and location where fat is stored. It varies between individuals and can impact overall health and disease risk. Two main types of fat distribution are visceral fat and subcutaneous fat.
- Visceral Fat:
- Location: Visceral fat is located deep within the abdominal cavity, surrounding internal organs such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines.
- Characteristics: Visceral fat is metabolically active and releases fatty acids and inflammatory substances into the bloodstream. It plays a role in insulin resistance, inflammation, and metabolic dysfunction.
- Health Implications: Excess visceral fat is associated with an increased risk of various health problems, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and certain cancers. It is often referred to as “deep belly fat” and is considered more harmful than subcutaneous fat.
- Subcutaneous Fat:
- Location: Subcutaneous fat is found directly beneath the skin, covering areas such as the abdomen, thighs, hips, and buttocks.
- Characteristics: Subcutaneous fat serves as insulation, energy storage, and protection for the body. It is less metabolically active than visceral fat but still plays a role in hormone regulation and body temperature regulation.
- Health Implications: While excess subcutaneous fat may contribute to cosmetic concerns such as body shape and appearance, it is generally less harmful to health compared to visceral fat. However, excessive subcutaneous fat accumulation can still be associated with increased risk of obesity-related conditions such as insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease.
Fat Cells and Fat Storage: Factors Influencing Fat Distribution:
- Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in determining an individual’s fat distribution pattern. Some people may have a predisposition to store more fat in certain areas of the body, such as the abdomen or thighs.
- Hormones: Hormones such as insulin, cortisol, estrogen, and testosterone influence fat distribution. For example, high levels of cortisol, often associated with chronic stress, can promote visceral fat accumulation.
- Age: Fat distribution tends to change with age, with a tendency to accumulate more visceral fat and lose subcutaneous fat as individuals get older.
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet, physical activity, sleep patterns, and stress levels can all impact fat distribution. Diets high in refined carbohydrates and sugars, sedentary lifestyles, poor sleep quality, and chronic stress may contribute to visceral fat accumulation.
Understanding fat distribution and its implications can help individuals make lifestyle choices to support healthy body composition and reduce the risk of obesity-related health conditions. A balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep are key components of maintaining optimal fat distribution and overall health.
Fat Cells and Fat Storage: How do I measure my body fat?
It quite difficult to measure body fat at home. However, there are ways that you can keep track of your weight.
- Scales: This option is simple and can give you an indication of weight increase and decrease. However, just relying on scales can be misleading. It is possible to lose water and muscle weight whilst not seeing a decrease in body fat.
- WHR – Waist to hip ratio measures the ratio of waist circumference to your hip. Medical professional use WHR to estimate how much fat is stored around your waist, hip, and buttocks.
- BIA – Bioelectrical impedance analysis. This method uses a device that sends a very weak electrical current around your body. As the current travels through fat muscle and water at different speeds, that rate of the currents return can estimate body composition. This method depends on the device used (pay for what you get) and the skill of the individual administering the test. BIA can be extremely sensitive, and things such as recent exercise, a full stomach and drinking caffeine before the test can throw the results off.
At Permanent Perfection, we provide BIA assessments during the consultation and process and throughout treatment if required. For BIA, we use Body Stat devices.
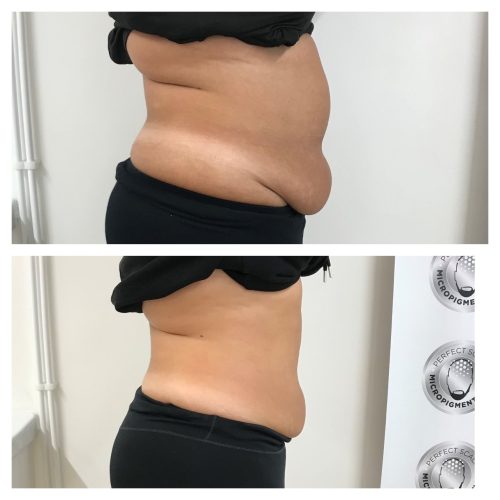
Fat Cells and Fat Storage: What can I do about excess fat?
Additonaly, at Permanent Perfection, we have a range of non-surgical fat removal technologies at our disposal. Our treatments can permanently remove fat cells. Once more, we are so passionate about supporting our customers to manage this that we offer at home personal training and diet planning to complement our BODY CONTOURING PACKAGES.
So, if you want to lose your unwanted fat cells and keep them off, what are you waiting for? GET IN TOUCH NOW!




Recent Comments